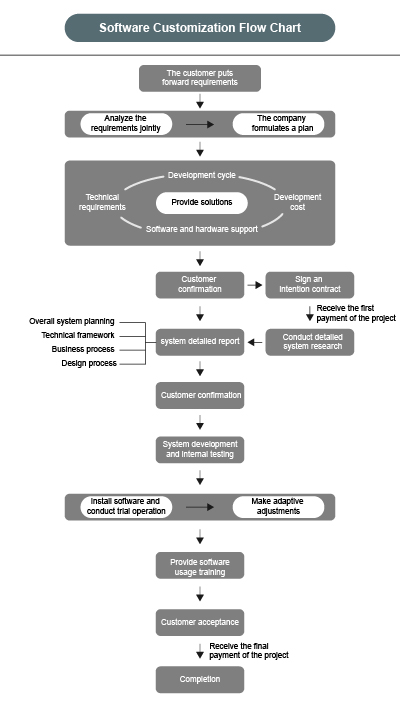
Software Customization Process
Demand Analysis: System analysts first understand user requirements and list major and minor functional modules of the system to be developed in Word. For some clear requirements, a few interfaces can be preliminarily defined. Then, based on their experience and requirements, they create a functional requirements document using WORD or related tools, which clearly details major and minor functional modules and related interfaces and functions. Finally, the system analyst reconfirms the requirements with the user. Outline Design: Developers conduct an outline design of the software system, considering aspects such as basic processing flow, organizational structure, module division, function allocation, interface design, operation design, data structure design, and error handling design, providing a foundation for detailed design.
Detailed Design: Based on the outline design, developers perform detailed design, describing main algorithms, data structures, class hierarchical structures, and call relationships of specific modules. The design considerations of each program in the software system are explained for coding and testing, ensuring that software requirements are fully allocated. The detailed design should be detailed enough for coding according to the report.
Coding: In this stage, developers start programming according to the "Detailed Design Report of Software System", realizing the functions of each module. In a standardized process, coding usually takes about 1/3 of the project time. Attention should be paid to the coordination and collaboration between different modules, as a small module problem may affect the overall progress. Mutual communication and emergency solutions during coding are crucial, as bugs are inevitable.
Test: The prepared system is tested. Software testing can be classified in multiple ways, such as internal and external testing by the test execution party, module testing and overall joint debugging by the testing scope, normal and abnormal condition testing by the test conditions, and full coverage and sampling testing by the input range. For a large software, 3 months to 1 year of external testing is common due to unpredictable problems. After testing, acceptance and final help documents are completed, and the project is considered over. Future upgrades and repairs are necessary to track the software's operation.
Software Delivery: Once the software passes the test, the developer submits the target installation program, database data dictionary, "User Installation Manual", "User Guide", demand report, design report, test report, etc. to the user. The "User Installation Manual" details the operating environment requirements, software definition and content, installation steps on the client, server, and middleware, and post-installation system configuration. The "User Guide" includes the use process, operation steps, business introduction, special prompts, and precautions of each software function, with examples if needed.
Acceptance: User acceptance is carried out.
Maintain: Based on changes in user needs or the environment, all or part of the application program is modified.
Copyright © 2024 K-Free Limited All rights reserved. 粵ICP備13026949號-3